Analyzing poppies to make better drugs
A team of researchers from the University of Calgary has uncovered new information about a class of plant enzymes that could have implications for the pharmaceutical industry.
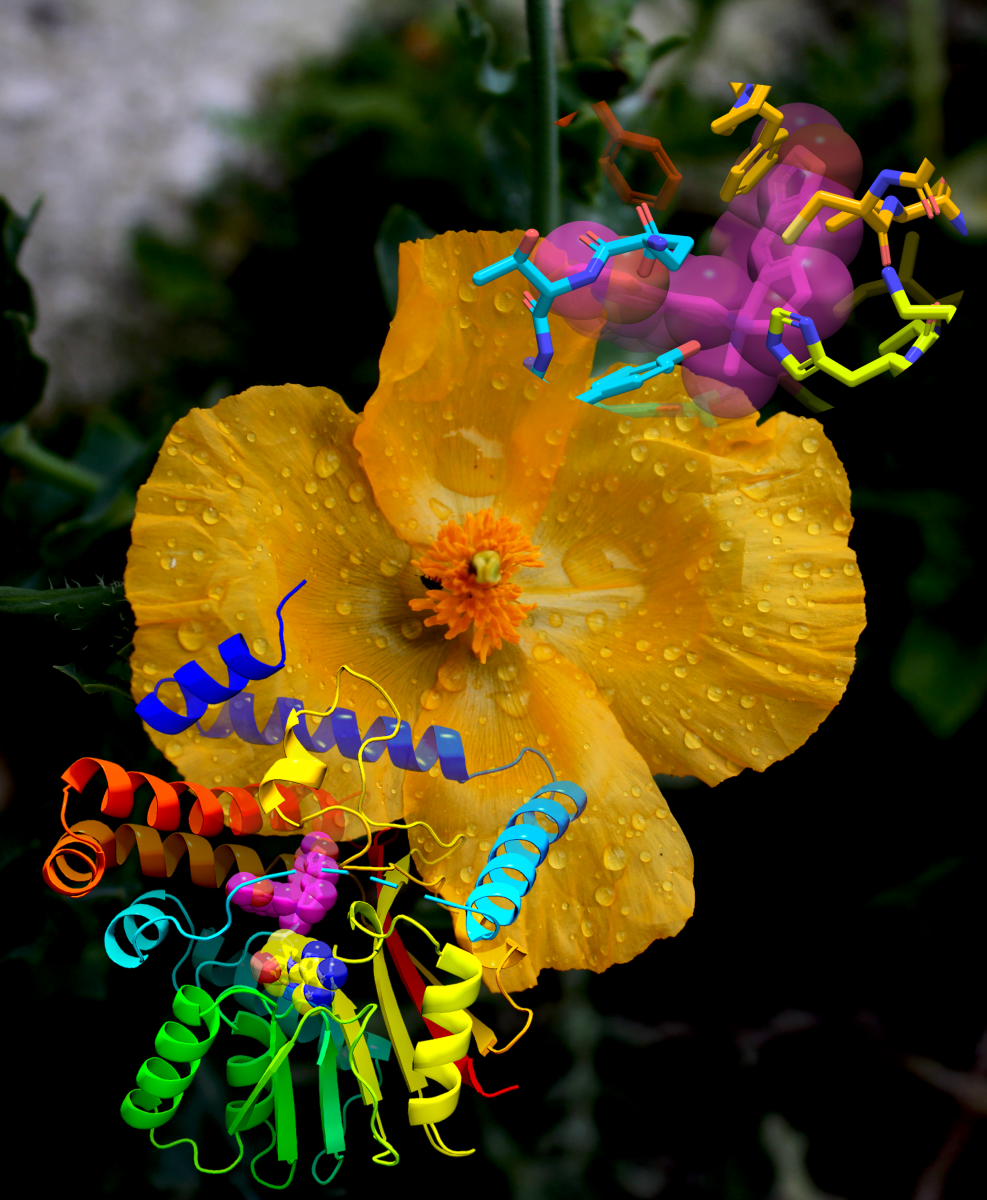
By Erin MatthewsAn overall view and active-site view of the crystal structure of proteins are shown superimposed on the background image of a yellow horned poppy. Image provided by David John Gibson, which is licensed under CC BY 2.0.
In a paper published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, the University of Clagary scientists explain how they revealed molecular details of an enzyme class that is central to the synthesis of many widely used pharmaceuticals, including the painkillers codeine and morphine.

The team used the Canadian Light Source at the University of Saskatchewan and the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory to better understand how the enzyme behaves, which is crucial for unleashing its potential to make novel medicines.
“Until this study, we didn’t know the key structural details of the enzyme. We learned from the structure of the enzyme bound to the product how the methylation reaction locks the product into a certain stereochemistry. It was completely unknown how the enzyme did that before we determined this structure,” corresponding author Dr. Kenneth Ng explained.
Stereochemistry is an important concept when it comes to safety and efficacy in drug design. A molecule can have a few different arrangements—similar to how your left hand is a mirror image of your right hand. These arrangements can lead to very different effects.
“There are a lot of classical examples where it can have a big effect,” lead author Dean Lang said. “Thalidomide is a famous historical example. When you have it in one stereochemical form it’s a good treatment for nausea, but in the opposite stereochemical form it can lead to birth defects.”
In this study, the stereoselectivity of the yellow horned poppy’s enzyme controls what substrates can interact, the products you will get, and how much medicinal compound you can extract from the plant.
Understanding how key enzymes behave can help bioengineers to optimize their drug production and allow researchers to explore new or rare compounds
“Aside from understanding how the plant does amazing chemistry, we also want to be able to transplant its capacity into organisms that are easier to deal with, like yeast or bacteria, so that we can make these medicines in a way that’s similar to making beer or wine,” co-author Jeremy Morris said.
“We hope that will reduce the cost of these medicines and make them more accessible,” he added.
Dr. Peter Facchini, one of the senior authors in this study and a professor at the University of Calgary, is leading an effort to translate fundamental discoveries into commercial applications as the Chief Scientific Officer of Willow Biosciences, a company founded on technology developed at the University of Calgary.
“Plant-derived compounds, such as opiates and cannabinoids, have pharmaceutical and commercial value, so we are always looking for opportunities to patent and potentially commercialize technologies we develop,” Facchini said.
He also discussed the value foundational academic research has for industrial applications.
“We understand pretty well how the plant is efficiently utilizing certain enzymes to make high-value products. However, to make plant products in yeast you generally have to manipulate these enzymes because you have to get them to work in an organism that is only distantly related to plants.”
Dr. Facchini stressed the importance of the hard work done by researchers involved in this study and the strong collaboration between their respective labs. He is hopeful that their research could lead to new, effective drugs in the future.
For more information, contact:
Victoria Schramm
Communications Coordinator
Canadian Light Source, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan
306-657-3516
victoria.schramm@lightsource.ca
Or
Erin Guiltenane
Communications Advisor
University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta
403-210-7584
eguilten@ucalgary.ca
